When’s the last time you heard the term data-driven? A day ago? Maybe a week? It’s more than just a buzzword; it’s a way of life in digital marketing. Marketers depend on precise, reliable data to understand user behavior and optimize digital experiences. Central to this data-driven revolution is the crucial (yet often-overlooked) data layer. Read on to learn more about the data layer, its significance in digital analytics and data collection, and how to manage its challenges effectively.
What is a Data Layer?
The data layer is a structured data repository acting as a bridge between a website’s frontend and any digital marketing technology that collects data. Residing in the browser, it functions as a single location to push data, so that any marketing technology can consume and collect it.
The data layer is typically implemented via JavaScript and includes key-value pairs that capture and transmit information about user interactions, page content, and events. The information in the data layer is generally retained for the duration of the user’s browsing session but can be configured to persist longer if needed.
Primarily, the data layer is created for analytics and marketing technologies to ensure accurate data collection and reporting. However, its utility extends beyond these functions. It can also be used by personalization engines, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and other tools that require detailed user interaction data to provide tailored experiences and insights.
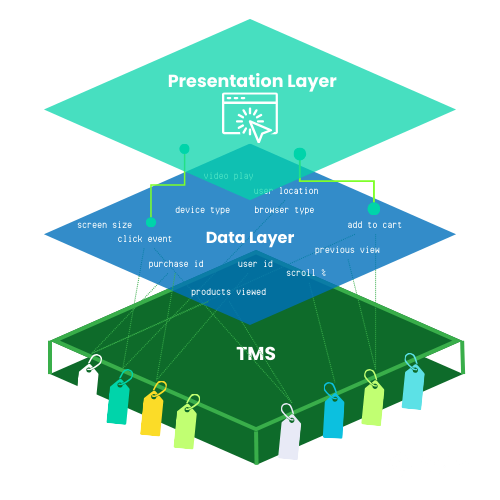
Image Caption: Illustration of where the data layer resides in the browser: between the user interface of a website and the tag management system containing marketing tags. Marketing tags are supercharged when they are able to access the rich user information available in the data layer.
What Does a Data Layer Provide?
The data layer is the foundation of modern digital analytics. It offers numerous benefits that collectively enhance the accuracy, efficiency, flexibility, and consistency of data collection and analysis.
Consistency, Efficiency, and Flexibility
Consistency: The data layer maintains a uniform data structure, which simplifies data collection, and by extension, analysis and comparison within the tools receiving the data. This consistency is vital for generating reliable insights and making data-driven decisions. For example, whether using Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, or another platform, the data layer ensures that the data collected is structured in a consistent format. This uniformity allows for easier comparison of performance metrics over time and across different marketing channels, providing a holistic view of the business’s digital performance.
Efficiency: By standardizing data collection, the data layer minimizes the possibility of discrepancies and errors. It streamlines the way data is gathered and transmitted across various tools and platforms. This efficiency reduces the need for repetitive coding and manual data adjustments.
Flexibility: The modular structure of the data layer allows for the seamless integration of new tools and technologies as analytics needs evolve. As businesses grow and their digital strategies become more sophisticated, the data layer can easily accommodate new data points and functionalities. For example, if an ecommerce site introduces a loyalty program, the data layer can be updated to track user engagement with this new feature, ensuring all relevant data is captured and analyzed.
The data layer makes pertinent information available in a consistent format to ALL marketing technologies. This means that the data only needs to be correct once for it to work properly in a multitude of different use cases.
What the Data Layer Enables
A well-implemented data layer contributes to a better experience for users and allows marketers to easily personalize the experience based on user attributes or behavior. By accurately capturing user behavior and preferences, businesses can tailor content, offers, and recommendations to individual users. For instance, if a user frequently views running shoes on an ecommerce site, the data layer can help deliver personalized product recommendations and targeted promotions, enhancing the user experience and increasing the likelihood of conversion.
Because of how it’s instantiated, the data layer enables real-time data analysis, which is essential for making timely decisions. When the data layer holds up-to-date information on user interactions and behaviors, businesses can quickly respond with relevant action. For example, if a particular product has been added to a user’s cart, the product information in the data layer enables marketers to identify this action in real time. If the user doesn’t complete the purchase, marketers are able to recapture the user’s interest quickly with relevant messaging, personalized promotions, or suggestions to supplement the product the user is already interested in purchasing.
Compliance and Data Governance
The data layer can play a role in ensuring data governance and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA as well. By centralizing data collection points and enforcing rules about what data can be collected, the data layer helps businesses stay compliant with legal requirements.
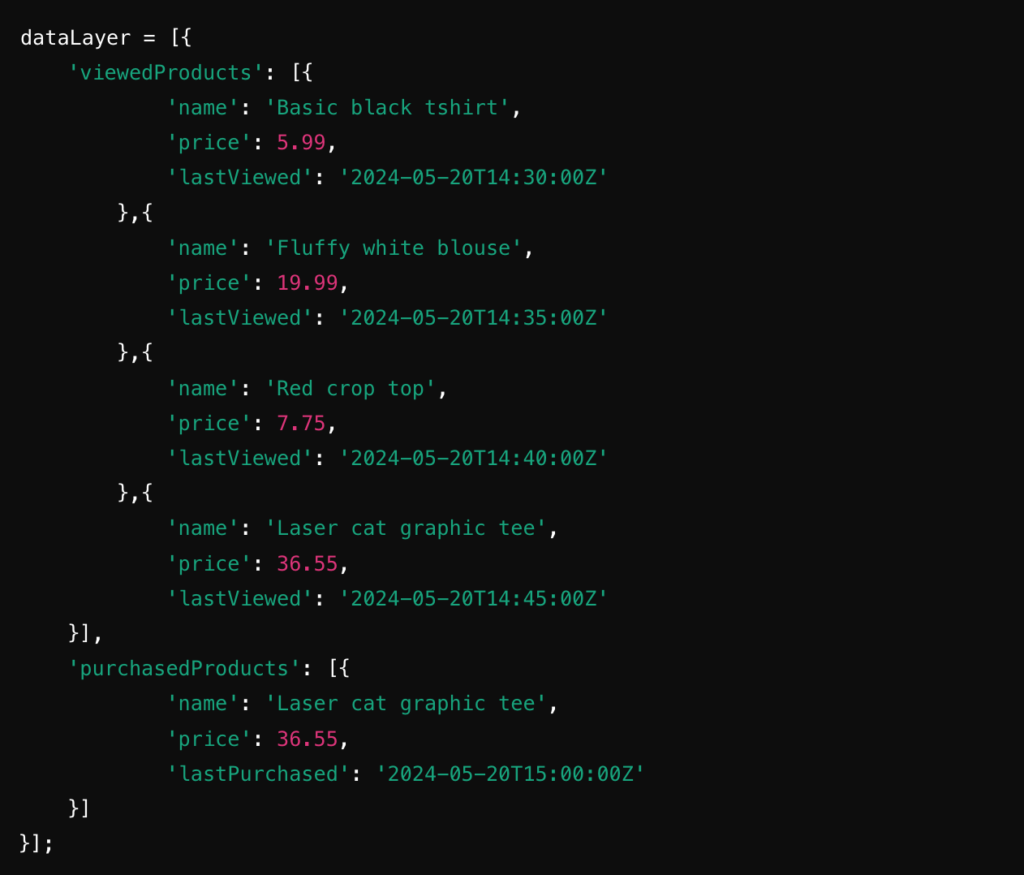 Image Caption: This basic data layer example shows an array of products that a website visitor has viewed, each product’s price at the time it was seen by the visitor, and information about which products were ultimately purchased. This flexible structure makes it easy to expand to support the data needs of the organization.
Image Caption: This basic data layer example shows an array of products that a website visitor has viewed, each product’s price at the time it was seen by the visitor, and information about which products were ultimately purchased. This flexible structure makes it easy to expand to support the data needs of the organization.
Who Manages the Data Layer?
The data layer is typically built by the same team or teams that handle web development. On the other hand, MarTech management (the tag management system and all marketing tags that reside within it) is typically separate from web development. The MarTech team will sometimes be a part of an IT organization, but sometimes rolls up to the Marketing org. This means that tag management and marketing technologies are often handled by a completely different team than the one that implements the data layer.
Sounds tough, right? It can be!
This means that a close collaboration between development and MarTech teams is vital. Typically the MarTech or marketing team (marketers) provides requirements to the development team (developers).
Data layer management tends to look something like this:
- Requirements for Key Data Points: Marketers define what data needs to be captured based on strategic goals, such as user actions that indicate engagement or conversion.
- Technical Implementation: Developers implement these data points directly in the website code, typically using JavaScript.
- Data Integrity: Developers are responsible for ensuring data accuracy and timeliness, preventing data errors or incorrect data capture.
- Maintenance and Scalability: Developers build the data layer, keeping in mind that it should accommodate changes as the website evolves, and structured to avoid costly overhauls.
- Documentation and Governance: Both teams create comprehensive documentation and establish data governance practices.
- Monitoring and Updates: Ongoing monitoring employed by the MarTech team ensures the data layer remains relevant and adheres to best practices. If updates are required, marketers submit them to the development team on an ad hoc basis.
TMS / Data Layer Integration
Most modern websites use tag management systems (TMS) like Google Tag Manager (GTM), Adobe Launch, or Tealium. The TMS and the tags housed within it interact directly with the data layer to access the information needed to capture analytics data and execute digital marketing strategies.
This workflow helps to streamline the integration of new tracking technologies and marketing tools without the need for hard-coded changes by developers. In the past, whenever new features were added to a website, the website team would need to work with the marketing team to understand specific tracking requirements for the addition. With the data layer, this process is simplified; the corresponding tags and triggers in the TMS are configured to interact with the data layer rather than scouring page code. This ensures that all user interactions are captured in one place and sent to the appropriate analytics and marketing platforms.
The TMS acts like a translator for the data in the data layer, ensuring the tags being deployed receive the data in the specific format they require. Each tag within the TMS may need data presented in different structures or formats to function correctly. By using a standardized data layer, the TMS can map the structured data to the format needed by each tag. This translation process ensures that tags operate efficiently and accurately, capturing all necessary user interactions and events without requiring extensive custom coding for each new tag or platform integration. This capability enhances the flexibility and scalability of the website’s analytics and marketing efforts, making it easier to adapt to new tools and technologies as they become available.
 Understanding the Data Layer: Monitoring and Documentation
Understanding the Data Layer: Monitoring and Documentation
As new types of data are incorporated into the data layer, continuous monitoring and documentation are crucial to prevent errors in the analytics being collected. This involves testing for data type integrity, ensuring data elements are not missing, and verifying that new additions do not conflict with or impede existing data collection.
You can test the data layer in a few different ways:
- Spot Checking: Use browser tools to manually verify data points.
- Regular Auditing: Conduct periodic audits to ensure ongoing accuracy.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring to catch issues in real time.
Did you know? You can install Sentinel Insights into your pre-production environments to test changes before they go live. Reach out to us to learn more about this use case!
Keeping your data layer documentation (commonly called a Data Layer Guide) up to date is also essential, especially when the structure of the data layer is frequently updated. This documentation should include:
- A clear description of each data element
- The source of each data element
- The purpose of each data element
Developers, marketers, and data analysts must communicate effectively to ensure everyone understands the changes and their impact on the data being collected and analyzed.
By following these practices, you can maintain a robust and efficient data layer, ensuring accurate data collection and reliable insights for better decision-making and optimized digital strategies.
Utilization – Beyond Data Collection
The data layer is not simply a browser-born database; it goes beyond that by structuring data in a way that makes complex analytical techniques possible. For instance, by compiling and organizing user interaction data into a coherent format, it paves the way for analysts and AI tools to apply statistical models and machine learning algorithms to predict user behavior or evaluate the effectiveness of different website designs.
Consumers today expect personalized, tailored experiences based on their behaviors and preferences. The data layer is a key component of a personalization strategy because it captures detailed user interactions, such as pages visited, products viewed, or content engaged with. Marketing teams can then use this data to create dynamic user profiles within customer relationship management (CRM) systems or personalization engines, which in turn drive customized content delivery, product recommendations, and targeted campaigns.
Attribution modeling is the process of determining which touchpoints or marketing channels contribute most to a desired outcome, such as a sale or conversion. The data layer collects the touchpoints across different channels (clicks from an email campaign, visits via a social media ad) in a unified format that attribution tools can analyze to assign credit to various marketing efforts. This precise data collection is critical for accurate attribution, which helps marketers optimize their budgets and strategies.
The data layer sends collected data to various analytics platforms like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, or custom-built analytics systems. For these platforms to generate actionable insights, the data must be accurate, complete, and relevant. The data layer’s structured approach ensures that all the right data points are captured and formatted correctly for these tools, which depend on consistent and standardized input to function optimally.
Management Challenges and Risks
As with any co-owned artifact, managing a data layer comes with a unique set of challenges:
- Technical Expertise: Implementing and maintaining a data layer demands strong web development and analytics knowledge. Developers must be proficient in JavaScript and familiar enough with analytics platforms to ensure it can accurately capture and transmit the data that marketing teams require.
- Multi-Team Alignment: Effective data layer management requires close collaboration between marketing operations, marketing technology, and development teams. Often, data-focused privacy and compliance teams are interested in the data layer as well. All teams must work together to ensure the data layer can support business objectives and is adaptable to support evolving needs.
- Consistency in Maintenance: Keeping the data layer consistent and current as the website evolves is crucial. Ongoing monitoring is necessary to maintain data accuracy and relevance, ensuring the data layer continues to support evolving digital marketing strategies.
But what happens if you get it wrong? What’s at risk? A neglected or mismanaged data layer can lead to significant issues and complexities:
- Inaccurate Insights: Flawed data distorts analysis, leading to poor decisions and ineffective strategies. Accurate data is essential for reliable analytics, and any errors in the data layer can compromise the quality of insights.
- Missed Opportunities: You can never restore data you never collected. Failure to capture essential interactions means lost insights. This can result in missed opportunities to optimize user experiences and marketing efforts, ultimately affecting campaign effectiveness and hurting the ROI of expensive marketing technologies.
- Operational Challenges: Integrating new tools or tracking new user behaviors becomes difficult with a poorly structured data layer. A robust data layer simplifies the addition of new technologies and ensures comprehensive tracking of user actions.
Checklist for Effective Data Layer Management
To ensure your organization manages its data layer effectively, follow these strategies:
- Focus on Collaboration: Promote robust communication between development and marketing teams to align the data layer with business goals. Ensure both teams understand each other’s requirements and work together seamlessly. If needed, host cross-team happy hours or Topgolf outings to get everyone on the same page.
- Establish and Maintain Accurate Documentation: Maintain a detailed Data Layer Guide containing all variables, events, and interactions within the data layer. This documentation should be accessible and regularly updated to reflect any changes or additions.
- Release Validation and Testing: Regularly check the data layer’s accuracy by manually auditing or inspecting it prior to release. After changes are live, conduct thorough testing to identify and fix any discrepancies or errors in data collection. To save time and provide wider coverage, deploy Sentinel Insights into your pre-production and production environments to monitor and validate data layer changes before and after they go live.
- Ongoing Auditing and Monitoring: Conduct regular audits and employ continuous monitoring to ensure the data layer remains accurate and up-to-date with business needs. These practices will help maintain data integrity, and ensure you can promptly address any issues that arise.
- Invest in Education: Ensure the data layer and digital marketing stays top of mind with development teams by providing tailored training and resources. Ongoing education helps maintain engagement over the course of a digital transformation, and ensures all team members stay up-to-date with the latest best practices in data layer management.
By following this checklist, your organization can effectively manage its data layer, ensuring accurate data collection and reliable insights for better decision-making and optimized digital strategies.